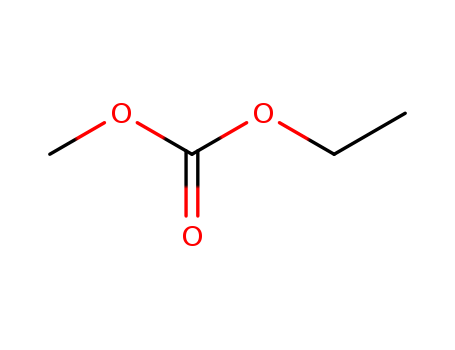
Ethyl methyl carbonate CAS NO.623-53-0
- FOB Price: USD: 1,500.00-1,500.00 /Kilogram Get Latest Price
- Min.Order: 10 Kilogram
- Payment Terms: T/T|Westem Union
- Available Specifications:
C4H8O3(10.0000-1000.0000)Kilogram
- Product Details
Keywords
Quick Details
- ProName: Ethyl methyl carbonate
- CasNo: 623-53-0
- Molecular Formula: C4H8O3
- Appearance: clear liquid
- Application: Ethyl Methyl Carbonate is a solvent of...
- DeliveryTime: 23days
- PackAge: 200kgs in drum
- Port: Douala
- ProductionCapacity: 1000 Metric Ton/Month
- Purity: C4H8O3
- Transportation: Air and Sea
- LimitNum: 10 Kilogram
Superiority
Carbonic acid (H2CO3) is a carbon-containing dibasic acid which has two acidic hydrogen atoms in the same molecule. The other common example of dibas…
Details
Carbonic acid (H2CO3) is a carbon-containing dibasic acid which has two acidic hydrogen atoms in the same molecule. The other common example of dibasic acid is sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Carbonic acid is formed in solution when its anhydride (carbon dioxide) is dissolved in water, existing only in equilibrium. The equilibrium is important for organisms to perform certain vital functions. The body fluids must maintain a constant pH. For example, blood must maintain a pH of close to 7.4 in order to carry oxygen from the lungs to cells. Carbonic acid has two acidic hydrogens and can lose one or two protons. The presence of pure carbonic acid is not possible as even a single molecule of water causes the carbonic acid to revert to carbon dioxide and water fairly quickly. Pure carbonic acid can be found if there is no water absolutely. Carbonic acid itself is a stronger acid than acetic acid or formic acid due to the influence of the electronegative oxygen substituent. Considering the equilibrium constant, however, the majority of the carbon dioxide is not converted into carbonic acid and so such solutions are fairly weak. Carbonic acid forms two series of salts when combined with positive or basic atoms or radicals; the hydrogencarbonate which contain the hydrogencarbonate ion HCO3- formed when the first proton is removed and the carbonate which contain the carbonate ion, CO32- formed when the second proton is removed. Hydrogencarbonates are also called bicarbonate or acid carbonate. Bicarbonates are formed under the presence of excess acid, while carbonates are formed when equivalent amounts of acid and base react. Most carbonic acid salts which are formed by reacting an inorganic base are the most basic industrial chemicals.